Comparative responses to cadmium toxicity of Arabidopsis thaliana mutant seedling (cad2) and wild type (col0)
CHAFFEI HAOUARI CHIRAZ1, SLATNI TARAK2, DJEMAL FATMA1, GOUIA HOUDA1 (Company / Faculté des Sciences de Tunis) 1Université Tunis El Manr, Faculté des Sciences de Tunis, Département de Biologie, 1060, Tunis, Tunisia 2 (Company / Centre de Biotechnologie Borj-Cédria) 1Université Tunis El Manr, Faculté des Sciences de Tunis, Département de Biologie, 1060,
1Université Tunis El Manr, Faculté des Sciences de Tunis, Département de Biologie, 1060,
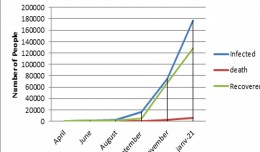
Abstract. The present study revealed the effects of cadmium on plant growth, anti-oxidant system characteristics, co-factors such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced (NADH) and oxided (NAD+), cadmium uptake and translocation and physiological responses of two Arabidopsis thaliana: the cad2 mutant and the col0 wild type. The inhibitory effect of cadmium on growth characteristics (dry and fresh weight and length of aerial and root parts) was more evident for the cad2 mutant, whereas least for the col0 wild type. The resistance of A. thaliana wild type (col0) to cadmium was mainly due to a lower cadmium absorption and translocation, thus keeping more effective activities of anti-oxidative enzymes and better co-factor balance state. Furthermore, hyperactivity of anti-oxidant enzymes also played an important role in protecting wild Arabidopsis thaliana from cadmium toxicity.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana, cadmium oxidative stress, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
 English
English  Français
Français  العربية
العربية