Selecting Suitable Sites for Wind Energy harvesting in Iraq using GIS Techniques
WEDYAN G. NASSIF1,2, DALILA ELHMAIDI1 , YASEEN K. Al-TIMIMI2
1 Thermal Radiation Research Unit ,Faculty of Sciences of Tunis ,University of Tunis El Manar, 2092 , Tunis. Tunisia
2Department of Atmospheric Science, College of Science, Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad, Iraq
*Corresponding author’s email :wedyan.atmsc@uomustansiriyah.edu.iq
dalila.elhmaidi@fst.utm.tn
yaseen.altimimi.atmsc @uomustansiriyah.edu.iq
Abstract
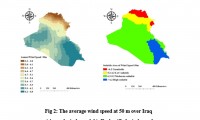
Wind energy is energy extracted from the kinetic energy of the wind by using wind turbines to produce electric energy. Wind energy is one of the most important types of renewable energy that has been widely used as an alternative to fossil fuels. It is abundant and renewable energy, but its availability varies from one location to another. The study aims to identify the best sites for wind energy in Iraq in order to produce the needed future energy from renewable sources. Multi-criteria analysis was used to determine the most suitable sites for harvesting wind energy using Geographic Information System (GIS). The most important data collected was climatic data and which includes a RASTER file of annual wind speed, temperatures, precipitation. soil moisture and NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), covering the study area over the past forty years., In addition, the shape file was used for each (distance from power lines, roads, Cities, slopes, and land use), where an appropriate model based on geographic information systems was produced when a set of raster data sets were classified and overlayed by the weighted overlay tool in Spatial Analysis Tools in ArcGIS 10.7.1. The results indicated that the best suitable sites for harvesting wind energy are located in the southeastern regions of Iraq. It is characterized by wind activity with a speed of more than 6.2 m / s. On the other hand, these areas are close to power transmission lines, roads, and slopes are moderate. Therefore, these areas were considered suitable for wind farms. Moreover, areas with a high suitability index cover 1% of the total area, which is an important indicator of wind energy harvesting potential in Iraq. The area with a moderate suitability index covers 71%, and the low suitability index was 15%, while 13% of unsuitable have been identified.
Key words: Wind Energy (WE), Multi-criteria, GIS, Iraq.
 English
English  Français
Français  العربية
العربية